You might be unknowingly making several AI search optimization mistakes that are quietly eroding your visibility right now. This article reveals the specific issues that prevent language models from referencing your content, confuse AI crawlers about your site structure, and cause your pages to disappear from AI-powered search results. It also provides actionable guidance through practical answer engine optimization solutions.
Why keyword stuffing fails in AI search optimization
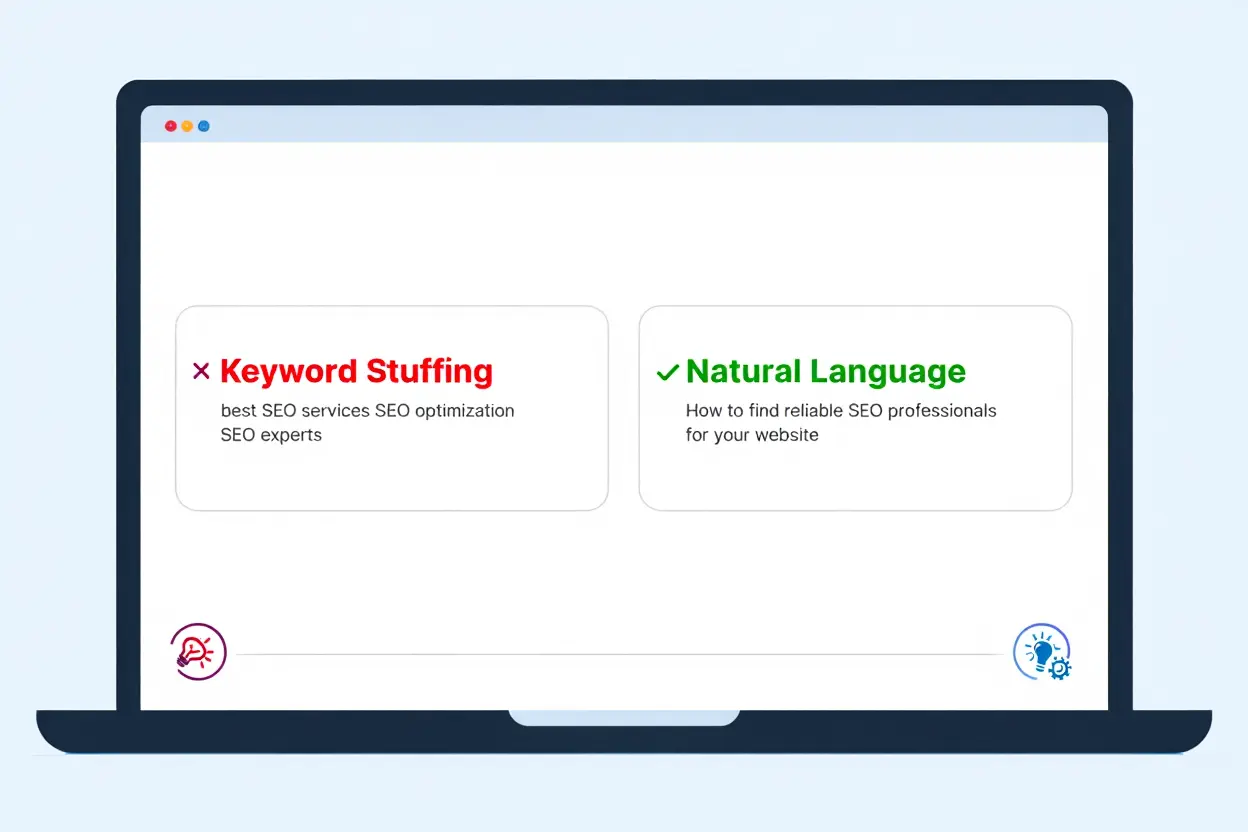
Keyword stuffing ruins your chances of appearing in conversational search results because language models prioritize understanding natural language and user intent rather than rigid keyword frequency. When you force keywords awkwardly into sentences, the text loses clarity and context. As a result, AI systems detect the unnatural tone and downgrade your content entirely.
How AI models prioritize conversational intent over keywords
Your AI search optimization strategy must shift from exact-match keywords to aligning with user intent. Modern models analyze entities, relationships, and the actual questions people ask—not just raw keyword density. For example, a query like “What sneakers are best for the environment?” carries more weight than repeatedly typing “eco-friendly sneakers.”
- Intent-driven structure: Organize information around core questions, incorporating sub-questions that reflect the natural language patterns people use in voice or chat searches.
- Synonym integration: Seamlessly include synonyms and related terms so keywords feel organic rather than forced.
- Entity recognition: Emphasize relevant entities—such as brands, materials, or concepts—to strengthen semantic authority and improve clarity for AI systems.
Before publishing, test new pages with AI prompt simulators to confirm that language models can extract direct answers accurately. If tools like ChatGPT or Claude struggle to cite your content correctly, restructure the page now to prevent costly losses in visibility later.
Testing content with AI prompt simulators before publishing
Put every draft through AI search user behavior simulations by prompting models with real audience queries. If the AI can’t pull a clear answer from your content, refine the structure, add more context, and reinforce key entities until the extraction works smoothly.
- Simulation testing: Use free AI tools to check if your page answers target queries clearly, completely, and without requiring extra guesswork.
- Extraction verification: Ensure key facts, stats, and conclusions can be quoted directly from your text.
- Clarity assessment: Eliminate ambiguous pronouns or vague references that might confuse AI and prevent accurate information retrieval.
Since real user queries constantly evolve, relying on a single static prompt is shortsighted. Cover a variety of question formats—comparisons, pros and cons, how-to guides, FAQs—within each topic cluster to satisfy diverse user intent patterns and avoid common AI search optimization mistakes.
Covering topic clusters instead of static sample prompts
A unified content strategy that groups related content like comparisons, lists, tutorials, and troubleshooting under a single pillar topic improves your chances of being cited across multiple contexts. This broad approach ensures your content meets a wide range of queries and strengthens entity recognition, clarity, and alignment with user intent throughout the search journey.
AI search tracking tools uncover the actual phrases people use, revealing optimization mistakes that traditional keyword research often misses. Monitor a broad spectrum of related queries—not just primary keywords—to detect patterns in AI search user behavior and keep your content prepared for future algorithm updates.
Missing structured data blocks AI answer extraction
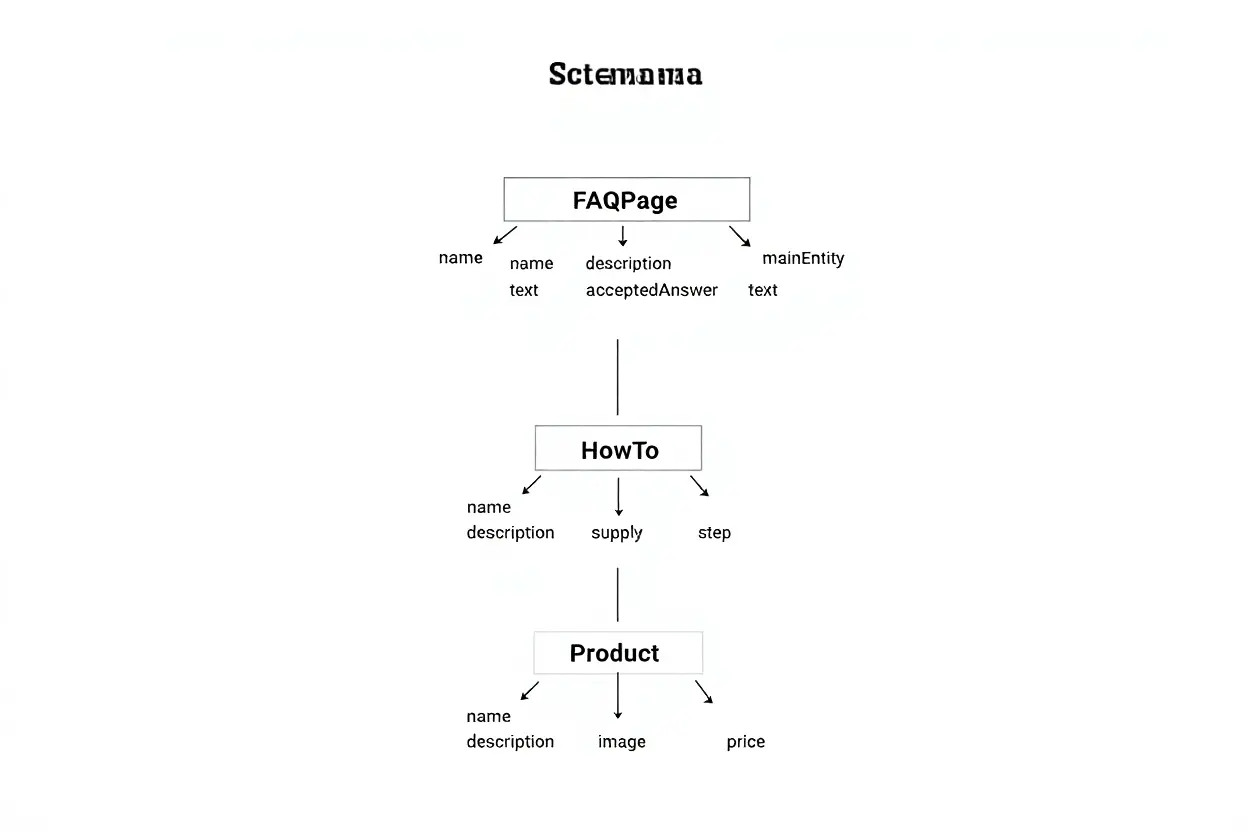
Without proper schema markup, AI crawlers find it significantly harder to pull answers for potential citations, which directly hurts your content's visibility. Think of structured data as a translator that bridges the gap between raw HTML and advanced language models, clarifying your content's purpose, accuracy, and authority for them. Neglecting this critical layer is one of the most damaging common AI search optimization mistakes because it creates a fundamental barrier that stops answer engines from featuring your work.
Why JSON-LD schema is essential for AI citations
JSON-LD structured data is the native tongue of modern AI systems; it converts unstructured web pages into clearly labeled blocks of knowledge. Proper schema markup sends unmistakable signals about your page's nature—whether it's a product review, an FAQ, a how-to guide, and so on—while also exposing key details like prices, ratings, and answers in a format machines easily understand. This clear structure reduces the chance of AI hallucinations, increases the likelihood of your content being cited, and eliminates numerous search optimization mistakes that stem from incomplete or flawed markup.
- FAQPage schema: Packages questions and their direct answers, enabling language models to quote them verbatim without misinterpreting the surrounding context.
- Product schema: Clearly communicates critical data like price, availability, reviews, and ratings, which minimizes the risk of hallucination and bolsters factual reliability.
- HowTo schema: Breaks down a process into defined steps, allowing AI to reference instructions with precision instead of providing a vague summary.
- Organization schema: Builds entity authority by linking to business details and credentials, thereby reinforcing crucial E-E-A-T trust signals.
Inconsistent schema implementation across your site will confuse language models and fragment your authority signals. For instance, if one product page has complete structured data but another is missing key fields, the AI model's confidence in your site's overall reliability plummets. To prevent this, standardize your implementation process and conduct quarterly audits to find new pages lacking markup or to fix any optimization mistakes that were introduced during updates.
Common schema validation errors that hurt AI visibility
Validation errors act as locked doors for AI crawlers, barring them from accessing your essential structured data and severely crippling your AI search optimization efforts. Empty required fields, incorrect property types, or malformed JSON code all prevent language models from trusting the facts on your page. Always use tools like the Rich Results Test or Bing Structured Data Validator before publishing to avoid repeating these common AI search optimization mistakes.
- Missing required properties: Omitting fields like name, description, or specific answer texts causes validation to fail and completely destroys any chance of a citation.
- Incorrect schema types: Using a Product schema for a service page or an FAQPage schema for a tutorial confuses the AI about your content's intent and reduces its perceived relevance.
- Malformed JSON syntax: Simple errors like misplaced commas or brackets break the code, rendering your structured data completely invisible to both crawlers and validators.
Older formats like microdata and RDFa lack support on newer platforms such as Google AI Overviews and Perplexity. A full migration to JSON-LD is now critical, as it is the format prioritized by every major language model. Treating this upgrade as mandatory is a vital step to avoid future AI search optimization mistakes and prevent easily avoidable search optimization mistakes.
Linking entities hierarchically for better AI understanding
Entities almost never exist in isolation; they form interconnected networks that provide rich context and clarify relationships for AI. By linking a product to its brand entity, that brand to independent reviews, and those reviews to the credentials of verified authors, you build a multi-layered structure that language models can instantly recognize and trust. This strategy powerfully strengthens your authority signals and supports generative AI errors research by creating transparent chains of evidence.
A well-designed schema markup that maps out connections (e.g., Product → Brand → Certifications → Expert Review → Author) constructs a cohesive framework of entities. These interconnected signals vastly improve common AI search optimization performance. This is because the models can grasp the full context of the information, not just isolated facts, which dramatically increases the chance of citation while reducing AI search optimization mistakes.
Poor content formatting prevents zero-click AI citations
How you format your content determines whether language models will quote you directly or invent information to fill in the gaps. When key facts are buried in dense paragraphs, lack clear headings, or mix unrelated ideas, AI systems struggle to extract concise answers for accurate citations. These formatting issues are at the root of the most common AI search frustrations, preventing zero-click answers and weakening alignment with search queries. Topic cluster errors often stem from poor internal structure within supporting articles, causing AI to overlook them during AI search traffic analysis.
Placing concise answers in the first 150 words
To ensure AI citations, your zero-click answers must appear within the first 150 words—otherwise, your page might never get quoted. Start with a direct 40-60 word response to the main question, then follow up with brief context that expands on your initial claim. This answer-first approach significantly enhances AI search optimization, allowing common AI search systems to quickly gather verified data without endless scanning.
- Answer-first structure: Open with a 40-60 word summary that directly addresses the primary query, then move into supporting context and more detailed sections.
- Direct phrasing: State your conclusions clearly, avoiding vague language that can reduce clarity and hurt extraction accuracy.
- Summary box reinforcement: Repeat the core answer at the end of the page to provide an additional, easily accessible extraction point.
| Content Element | Optimal Placement | Word Count | AI Impact |
| Direct answer | First 150 words | 40-60 words | Boosts immediate extraction and citation odds |
| Brief explanation | Sentences 3-4 after answer | 50-80 words | Adds context without overwhelming models |
| Supporting details | H2/H3 sections after intro | 200+ words total | Provides depth for expanded queries |
| Summary box | Page conclusion | 40-60 words | Reinforces message and offers secondary hook |
Using heading hierarchy for AI question matching
A clear hierarchy of H1, H2, and H3 headings allows AI models to break your content into reusable question-and-answer blocks with minimal effort. Write your H2 headings as actual search queries to instantly signal relevance, then use H3 tags for more specific points that add deeper context. This intentional structure increases citation frequency and strengthens AI search traffic analysis, since each section maintains clarity even when taken out of context.
- Question-based H2s: Frame subheadings as full queries—for example, “How do you identify sustainable materials?”—rather than using vague or generic labels.
- H3 granularity: Divide complex answers into smaller, standalone units so AI can quote the exact portion that delivers concise answers.
- Logical flow: Organize headings to guide both readers and algorithms smoothly, avoiding gaps in context during information extraction.
- Keyword relevance: Incorporate natural keyword variations into your headings to support both human readability and algorithmic matching.
Bullet points, numbered lists, and tables create visual separation, making it easier for AI to identify and cite individual facts. Short sentences and plenty of white space improve clarity and reduce the risk of AI hallucinations, as models can capture distinct ideas without having to guess at missing context. Replace long blocks of text with scannable, structured elements to deliver precise information that satisfies user queries and promotes accurate zero-click answers.
